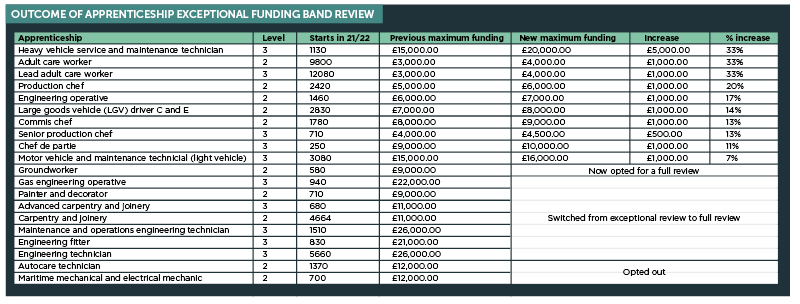
Two popular adult care apprenticeships have received a 33 per cent funding uplift this week, but training providers have warned that won’t be enough to keep up with rising costs.
Skill minister Robert Halfon revealed the long-awaited outcome of the Institute for Apprenticeships and Technical Education’s exceptional funding band review (which has been beset with delays) at this week’s Association of Employment and Learning Providers national conference in London.
Announcing funding increases for ten apprenticeships standards, Halfon said: “We know that inflation is hurting our whole economy, and I know this is putting pressure on you as you deliver high-quality training. It is affecting the costs of energy, materials, food, and tutor salaries.
“We are alive to the cost pressures you are facing to deliver high-quality apprenticeships, and I hope I’ve shown we will take action to support you,” he said.
Twenty apprenticeships were initially in scope for funding uplifts through the exceptional review when it was finally launched in January, having been originally announced last November. IfATE then passed its own planned end date for the review. It was supposed to have concluded in May.
AELP said lessons must be learned over the process.
Simon Ashworth, director of policy, said “The increase in adult care level 2 and level 3 by a third is most welcome. However, there are still lessons that must be taken from this process. It has simply taken far too long to get an outcome to a process that was meant to enable a speedy decision to be taken against the backdrop of unprecedented inflation rates.”
In March it was revealed that 10 of the twenty apprenticeships were opted out of the review by their employer-led trailblazer groups who instead wanted a full review including content, funding and assessment.
One of those that had opted out was the level 3 heavy vehicle service and maintenance technician apprenticeship. However, that apprenticeship, alongside the level 2 adult care worker and level 3 lead adult care worker, received one of the largest funding increases this week.
From Monday, when the announcement was made, funding for heavy vehicle apprentices increased from £15,000 to £20,000 and the two adult care standards increased from £3,000 to £4,000.
Apprenticeships for production chefs, senior production chefs and commis chefs were increased by one funding band. As were other popular apprenticeships, such as the level 2 engineering operative, level 3 motor vehicle and maintenance technician, and the level 2 large goods vehicle driver.
IfATE chief executive, Jennifer Coupland, said while the funding uplifts “should have a positive impact on providers and learners” she was “sorry the process has taken longer than anyone would have hoped for.”
It was also revealed that trailblazer groups for two of the remaining ten standards have opted out entirely because “they decided they didn’t need funding” according to Coupland.
Those are the level 2 maritime mechanical and electrical mechanic apprenticeship and the level 2 autocare technician, both funded at £12,000.
HGV apprenticeships funding row
Heavy vehicle service and maintenance was a surprise entry, considering it had been removed by its employer trailblazer group from the exceptional review in favour of a normal review.
An IfATE spokesperson told FE Week that this apprenticeship had completed a full standard review “at pace” alongside the other ten standards.
“This sector literally keeps our economy moving. It is right that we mitigate the significant cost increases it is facing, and recognise the critical contribution it makes to productivity,” Halfon said.
However, one training provider said it was “hugely disappointed” that the apprenticeship didn’t receive a larger increase to account for the standard being subjected to under-funding “by mistake” for the last four years.
Sue Pittock, chief executive of Remit Training, told FE Week that the funding band should be £26,000, similar to other advanced engineering apprenticeships, to run “a quality HGV programme safely”.
Pittcok also took aim at the minister’s claim that funding for that apprenticeship was increasing by 33 per cent.
“The funding band for HGV was in fact £18,000 back in 2010, but was reduced to £15,000 in 2019, based on an error which IfATE acknowledge it made. In reality, at £20,000, we are behind where were back in 2010 once you add EPA costs and inflation.
“Things have changed materially in the 13 years since 2010 and our costs of delivery have increased exponentially,” Pittock said.
An IfATE spokesperson said that the organisation is “satisfied that its published processes were followed at all times and the decision to reduce the funding of HGV tech in 2019 to £15,000 was based on the evidence presented.”
However, in 2022, the spokesperson added, IfATE “became aware some of the information put forward in 2019 could have been inaccurate.”
“The most appropriate response was to re-run the funding band process using refreshed evidence, which has now been concluded,” they added.
Time to care
Inadequate funding for adult care apprenticeships has long been criticised by the health and training sectors. Several training providers that have specialised in care training have gone bust in recent times, notably Qube Learning, Quest Vocational Training, and GP Strategies Training
News of the £1000 funding increase this week was welcomed by the sector, but some have said it is still not enough.
Ian Bamford, chief operating officer at Paragon Skills and an AELP board member, told FE Week the adult care uplift was “really positive for the sector” but suggested a further increase to £5,000 was needed.
“We’ve had to increase staff salaries, so we’re now having to pay probably in the region of £28-£30,000 for an adult care tutor. A year to 18 months ago, that was £24-25,000, and we’ve had to swallow that cost.
“We’re also looking for a more digitally rich and innovative curriculum. On £3,000 you just can’t do that. So, this [uplift] allows us to be able to put investment in our programmes,” Bamford said.
Bamford said he believed there are discussions about a further review for a new care apprenticeship standard being pitched at a £5,000 funding band, “which is where it needs to be.”
Another large training provider in the care training sector, Lifetime Training, said the increase was “a step in the right direction.”
Matt Robinson, Lifetime’s commercial director, told FE Week that the “increased funding bands will greatly benefit our apprenticeships, allowing us to invest in delivering high-quality programmes despite mounting inflationary cost pressures”.