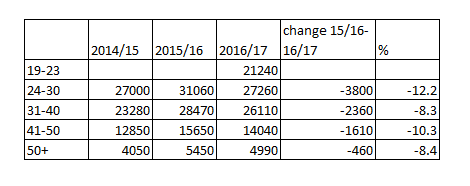
Applications for FE loans were down in 2016/17 for all age-groups they were available to in previous years.
The total number of applications “received” increased marginally from 80,650 in 2015/16, to 93,660 for 2016/17, according to latest figures published by the Department for Education this morning.
However, this is taking into account 21,240 from 19 to 23-year-olds, who were able to apply for FE loans for the first time from August last year.
All other age groups were down.
The 2016/17 figure for 24 to 30-year-olds was 27,260 – down 12 per cent from 31,060 the previous academic year.
The corresponding drops were 8 per cent for 31 to 40-year-olds (from 28,470 to 26,110); 10 per cent for 41 to 50-year-olds (from 15,650 to 14,040); and 8 per cent for those aged 50-plus (from 5,450 to 4,990).
Mark Dawe, Association of Employment and Learning Providers’ boss, said the fall in applications was linked to new restrictions on loans-funded provision.
The new limits, which include a ban on subcontracted loans provision and growth caps, were brought in by the Education and Skills Funding Agency in 2016/17 following a series of scandals – exposed by FE Week – in which loans-funded learners were left with massive debts but no courses after their providers, including John Frank Training, Edudo Ltd and Focus Training and Development Ltd, went bust.
“Some independent providers can and want to deliver more loans-funded learning but growth is capped,” Mr Dawe said today, a situation that he described as “unfortunate, although we understand the reasons for the agency’s caution”.
“But even more important and concerning is that the requirements on new entrants gaining access to the loans market are very tight and AELP would like to see them reviewed,” he added.
It comes after FE Week revealed last month, through a freedom of information response, that a massive 58 per cent of FE loans funding – amounting to almost £1 billion – had not been spent since 2013.
The Student Loans Company, which processes advanced learner loans for the government, revealed that only £652 million in loan-funded provision had actually been delivered since 2013, compared to £1.56 billion in allocations.
FE loans, originally known as 24+ loans, were introduced in 2013/14 for learners studying courses at levels three or four and aged 24 and older.
Their introduction corresponded with a fall in adults studying at levels three and four+, from 273,400 in 2012/13 to 195,200 in 2013/14, according to the DfE’s own statistics.
That number had fallen further still, to 169,400 by 2015/16.
Yet loan eligibility was expanded in 2016/17 to include 19- to 23-year-olds, and courses at levels five and six.
FE Week asked the DfE if it was concerned about the fall in applications for all 24+ age groups. In response, a spokesperson said: “Advanced learner loans are available to thousands of adults wishing to retrain, helping them to meet upfront fees and removing one of the main barriers to learning.
“It is vital we build the skilled workforce that business and the country needs to ensure we can compete across the world and adult education is part of this. We will continue to work with colleges and training providers to raise the profile of advanced learner loans.”
Loan applications received by the DfE from 2014/15 to 20167/17 (according to official government statistics):